Designing Jigs and Fixtures
- Home
- Blog Details
- June 12 2019
- admin
The design of jigs and fixtures is dependent on numerous factors which are analysed to achieve optimum output. Jigs should be made of rigid light materials to facilitate secure handling, as it has to be rotated severally to enable holes to be drilled from different angles. It is recommended that four feet should be provided for jigs that are not bolted on the machine tool, to enable the jig to wobble if not well positioned on the table and thereby alert the operator. Drill jigs provide procedures for proper location of the work-piece concerning the cutting tool, tightly clamp and rigidly support the work-piece during machining, and also guide the tool position and fasten the jig on the machine tool.
To achieve their expected objectives, jigs and fixtures consist of many elements:
- Frame or body and base which has features for clamping
- The accuracy and availability of indexing systems or plates
- The extent of automation, capacity, and type of machine tool where jigs and fixtures will be employed
- Bushes and tool guiding frames for jigs
- The availability of locating devices in the machine for blank orientation and suitable positioning
- Auxiliary elements
- The strength of the machine tool under consideration
- The precision level of the expected product
- Fastening parts
- The available safety mechanisms in the machine tool
- The study of the fluctuation level of the machine tool
The factors below are to be reflected upon during design, production, and assembly of jigs and fixtures due to the targeted increase in throughput, quality of products, interchangeability, and more accuracy.
- Guiding of tools for slim cutting tools like drills
- Type of operations
- Inspection requirements
- Provision of reliable, rigid, and robust reinforcement to the blank
- Production of jigs and fixtures with a minimum number of parts
- Fast and accurate location of the jig or fixture blank
- Rapid mounting and un-mounting of the work-piece from the jig or fixture
- Set up time reduction
- Standard and quality parts must be used
- Reduction of lead time
- Easy disposal of chips
- Enhanced flexibility
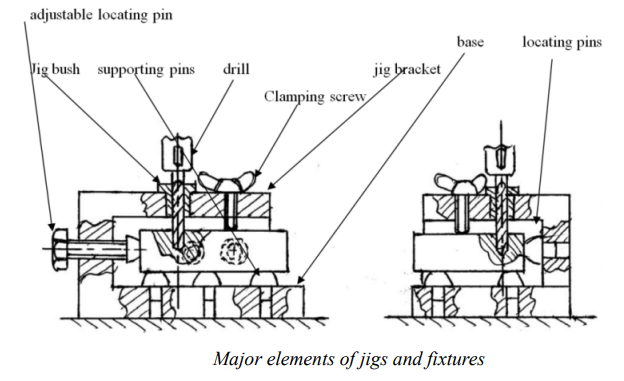
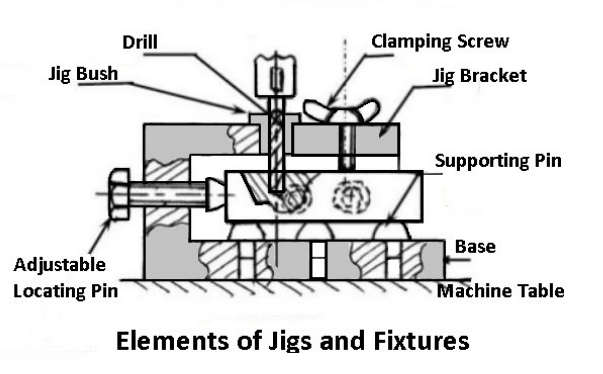
Elements of Jigs and Fixtures
The significant features of Jigs and Fixtures are:
The body: The body is the most outstanding element of jigs and fixtures. It is constructed by welding of different slabs and metals. After the fabrication, it is often heat-treated for stress reduction as its main objective is to accommodate and support the job.
Clamping devices: The clamping devices must be straightforward and easy to operate, without sacrificing efficiency and effectiveness. Apart from holding the work-piece firmly in place, the clamping devices are capable of withholding the strain of the cutting tool during operations. The need for clamping the work-piece on the jig or fixture is to apply pressure and press it against the locating components, thereby fastening it in the right position for the cutting tools.
Locating devices: Thepin is the most popular device applied for the location of work-piece in jigs and fixtures.The pin’s shank is press-fitted or driven into a jig or fixture. The locating width of the pin is made bigger than the shank to stop it from being pressed into the jig or fixture body because of the weight of the cutting tools or work-piece. It is made with hardened steel.
Jig bushing or tool guide:Guiding parts like jig bushings and templates are used to locate the cutting tool relative to the component being machined. Jig bushes are applied in drilling and boring, which must be wear resistant, interchangeable, and precise. Bushes are mainly made of a reliable grade of tool steel to ensure hardening at a low temperature and also reduce the risk of fire crackling.
Selection of Materials
There is a wide range of materials from where jigs and fixtures could be made, to resist tear and wear, the materials are often tempered and hardened. Also, phosphor bronze and other non-ferrous metals, as well as composites, and nylons for wear reduction of the mating parts, and damage prevention to the manufacturing part is used. Some of the materials are discussed below:
- Phosphor Bronze: phosphor bronze is used in the production of jigs and fixtures for processes that involve making of interchangeable nuts in clamping systems like vices, and also incorporated feedings that require screws. As the manufacturing of screws is costly and also wastes a lot of time, the reduction of their tear and wear is often achieved by using replaceable bronze mating nuts made with phosphor bronze.
- Die Steels: the three variants of die steel – high chromium (12 %), high carbon (1.5 to 2.3%), and cold working steels are applied in the production of jigs and fixtures for the making of thread forming rolls, as well as cutting of press tools. When alloyed with vanadium and molybdenum for it to retain toughness at very high temperature, die steels are applied in the fabrication of jigs and fixtures that are used in high-temperature work processes which include extrusion, forging, and casting processes.
- High-Speed Steels: High-speed steels which contain more quantity of tungsten and less quantity of chromium and vanadium have high toughness, hardness retention at high temperature, and excellent wear, tear and impact resistance. When tempered, they are applied in the production of jigs and fixtures for reaming, drilling, boring, and cutting operations.
- Carbon Steels: when tempered with oil, carbon steels are applied in the making of some jig and fixture parts which are exposed to tear and wear like the locators and jig bushes.
- Mild steels: Mild steel, which contains about 0.29% of Carbon, is very cheap and because of their easy availability is often the choicest material for the making of jigs of fixtures.
Other materials for the making of jigs and fixtures include Nylon and Fibre, steel castings, stainless steel, cast iron, high tensile steels, case hardening steels, and spring steels.
Reference
Charles ChikwenduOkpala, EzeanyimOkechukwu C “The Design and Need for Jigs and Fixtures in Manufacturing” Science Research.Vol. 3, No. 4, 2015, pp. 213-219. DOI: 10.11648/j.sr.20150304.19

