Energy Management System (EMS) for Manufacturing Visibility
What is powerCONNECT?
powerCONNECT is a Real-Time Energy Monitoring and Intelligence Platform built specifically for the manufacturing floor.
See how energy is utilized across your plant – live, clear, and in one centralized dashboard. powerCONNECT serves as a comprehensive EMIS, integrating with your existing energy meters to capture live data, visualize load patterns, and generate equipment-wise analytics. It does not control your machines; it gives you the clarity to manage your operations better.
How It Works
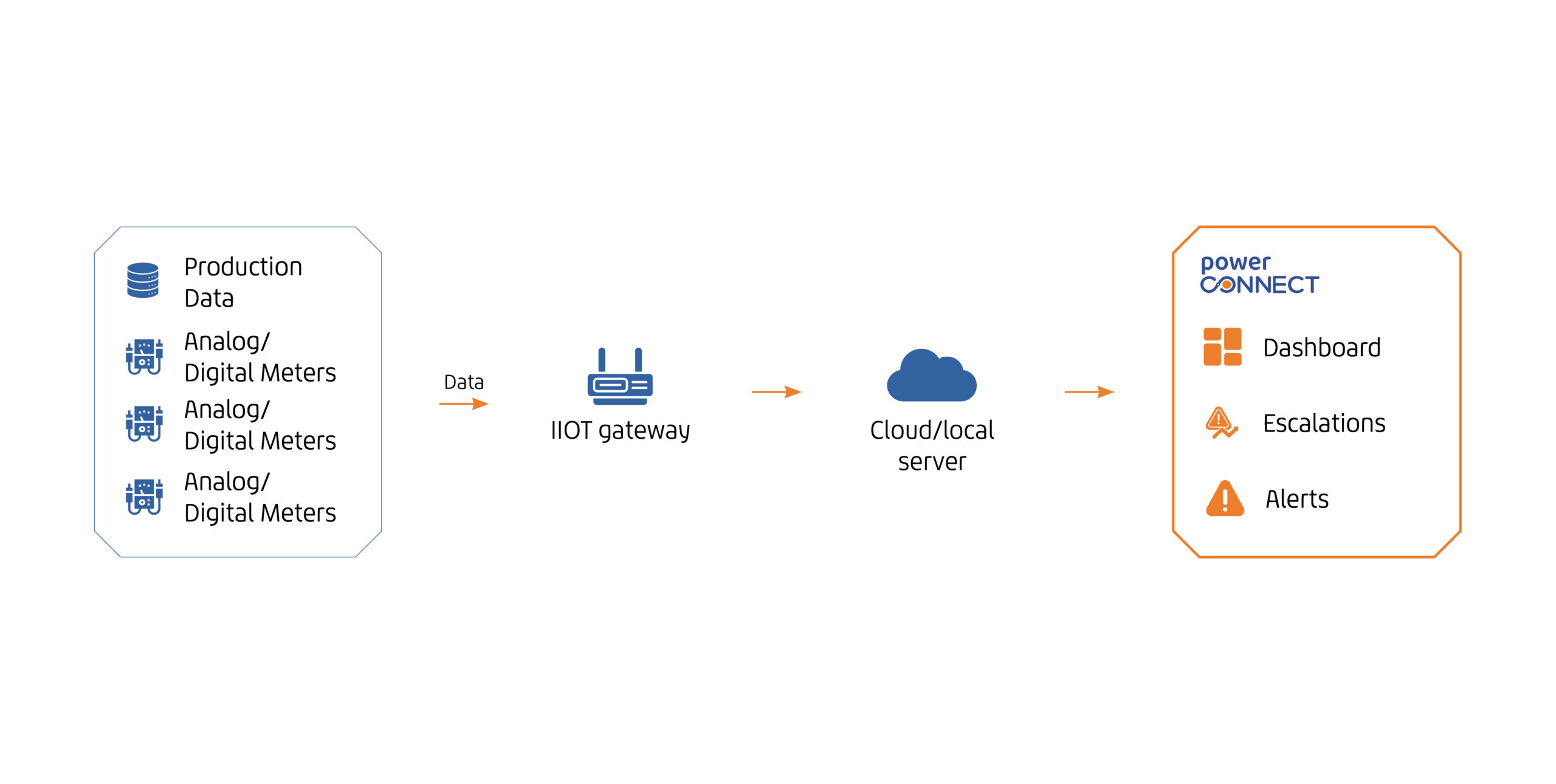
Connect
Seamlessly integrates with your existing energy meters via multi-protocol support for a unified data stream.
Monitor
Captures live energy data and visualizes it on a central dashboard to track consumption shift-wise, machine-wise, and section-wise.
Enhance
Identifies inefficiencies, spikes, and idle loads so you can take immediate action and avoid non-productive consumption.
Seamless Data Flow from Meters to Actionable Insights
The Visibility Gap: Why Energy Monitoring Matters
No Real-Time Visibility
Needed to optimize performance and prevent waste.
Manual Meter Readings
Prone to human error and reporting delays.
Load Factor Penalties
Expensive surcharges for unstable power demand.
Invisible Idle Waste
Machines consuming power even when not in production.
Delayed Reporting
Taking days to generate reports that should take seconds.
Deep Dive into Your Manufacturing Energy Data
Real-Time Electricity Consumption Dashboards
View live energy usage across the entire plant and respond to abnormal spikes before they impact your bottom line.
Machine-Wise & Section-Wise Tracking
Know exactly which equipment or departments are the highest energy consumers to optimize duty cycles and asset health.
Productive vs. Idle Energy Analytics
Automatically detect and isolate energy used during production versus energy wasted during idle time.
Load Factor Monitoring & Peak Demand Alerts
Track load stability to optimize usage and avoid utility penalties by setting custom thresholds.
Digital SLD & Meter Health
Visualize your plant's electrical network and monitor meter health with a Digital Single Line Diagram (SLD).
Designed for Energy-Intensive Industries
Steel Plants & Integrated Steel
Maximize energy-per-ton efficiency via precise energy consumption metrics. Boost primary production and reduce carbon intensity.
Rolling Mills
Eliminate process desynchronization waste by aligning motor-drive efficiency with real-time monitoring. Energy loss is often hidden within high-speed system inefficiencies.
Foundries
Recapture energy spend by isolating non-productive idle waste and optimizing the melting furnace. Furnaces account of nearly 55% of total energy consumption.
Automobile Manufacturing
Gain deep visibility into assembly line load patterns to eliminate robot standby waste. Improve the energy footprint of paint shop operations.
Heavy Process Industries
A unified, non-intrusive monitoring layer bridges legacy infrastructure and modern IoT. Ensure load stability across complex, high-demand manufacturing ecosystems.
Why Choose Prescient Technologies as Your EMS Partner?
Choosing an EMIS partner requires a balance of software expertise and deep industrial knowledge.
With a 25-year legacy in PLM and digital factory solutions, we work closely with your IT and operations teams to design solutions tailored to your factory layout and legacy systems.
From assessment and customization to implementation and training, we provide end-to-end support to ensure long-term performance and value.
Is powerCONNECT an automation control system?
No, powerCONNECT is a Monitoring & Intelligence platform. It provides the data and insights required for humans to make control decisions, but it does not automatically turn machines on or off.
What energy management KPIs can I track with powerCONNECT?
You can track critical KPIs such as Load Factor, Energy Per Ton, Idle Ratio, Power Factor, and specific consumption trends.
Featured Posts
Contact Us
Our experts will respond within 24 hours.