MES Supercharges Steel Production: How It Improves Factory Performance
Table of content Challenges in Steel Production Manufacturing How the MES System Improves Factory Performance and Mitigates Challenges Closing Thoughts In steel production manufacturing, the intricacies of management within the factory environment present daunting challenges. Each order placed for the batch is different and varies from client to client, necessitating careful preparation according to the outcome. While most steel mills have their own MES system, they are often tailored to the specific production needs and operating procedures. Some still operate with a lot of paperwork and manual documentation. Also the demanding nature of the steel industry necessitates a strategic approach to enhance operational efficiency in the plant to reduce waste and mitigate costs. It’s important to consider that even single digit percentage improvements in yield and efficiency in the steel production can translate to millions of dollars saved per year. Hence, MES systems customizable to the needs of individual units can make a significant difference. Challenges in Steel Production Manufacturing Steel production faces a number of challenges that starts from the level of global demand and trickles down to the complexity of running a steel mill. Unlike many other production processes, which are quite flexible from start to finish, steel production works with a lot of momentum. Errors are always expensive, and the costs could run in the millions. But here are major challenges in the steel industry looking from top down: Volatility of price and overcapacity of plants The global steel industry grapples with an oversupply conundrum, where production capacity significantly surpasses demand, fostering cutthroat competition and price volatility. In 2021, the sector witnessed a high steel production of 1.95 billion tons against a demand of 1.89 billion tons. Surplus production always exerts a notable downward force on prices in the market. Global Trade Challenges Trade policies meant to protect local industries, like tariffs and quotas, disrupt the global trade landscape, creating market distortions that hinder industry growth. In 2018, the United States implemented Section 232 tariffs, imposing a significant 25% duty on steel imports. This move reshaped global trade patterns, leaving a lasting impact on the industry’s dynamics. Slow Digital Transformation The steel industry lags in embracing digital technologies which impedes its operational optimization, efficiency enhancement, and cost reduction. Despite acknowledging the benefits of digital transformation, steel companies face sluggish adoption due to inherent implementation challenges. Environmental Challenges Steel production which constitutes approximately 7% of global emissions, emerges as a substantial contributor to greenhouse gasses. Stringent environmental regulations and the implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms elevate production costs, presenting challenges to the steel industry’s sustainability efforts. How the MES System Improves Factory Performance and Mitigates Challenges Here are some of the ways in which MES system can supercharge steel production: Enhanced Production intelligence MES seamlessly integrates your business, production, energy demands, and logistics data by linking equipment, control systems, applications, and databases. This enables the identification of production challenges, such as bottlenecks and quality issues, through dashboards and real-time performance information in production trend reports. Additionally, MES establishes a connection between the mill floor and your ERP systems, ensuring direct delivery of production reports populated with material consumption, quality, and process details. What it can also do is utilize Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) capabilities to optimize production planning and scheduling and align it with real demand in the market based on your inputs. This helps minimize excess inventory, and enable efficient planning for production, which contributes to price stabilization. Over-all Performance Improvement MES system improves productivity by tracking by providing essential metrics, such as overall equipment effectiveness and downtime analysis, and all this data is contextualized by shift, area, and production site. The integration of production data with diverse sets of parallel data, like energy consumption, enables comprehensive cross-referencing that can go a long way in monitoring energy consumption. Savings in terms of energy not only benefits directly but also helps make the process greener by reduction in the carbon footprint. Moreover, the combined data enables pinpointing productivity bottlenecks and strategically identifying areas for cost reduction. The system offers a holistic understanding of operational efficiency that aids in fine-tuning processes, minimizing downtime, and optimizing resource allocation for enhanced productivity. Precise Recipe Management Manual recipe development and entry and reliance on physical documents for workflow management are time-intensive tasks prone to errors. MES streamlines operations by enabling the creation and storage of recipes, standardizing procedures, and directly synchronizing order management with the ERP system. When a new order arrives, MES interfaces with the ERP to handle production schedules, quality, and operational settings. The system then generates precise work orders, optimizing sequences and executing them smoothly on the plant floor. This ensures that accurate recipe set-points are promptly transmitted to the control layer, facilitating automated and precise recipe execution at the furnaces. Improved Quality MES enhances operational efficiency by providing pre-designed workflows and instructions and aids operators in adhering to defined quality parameters. The system collects data at quality checkpoints and issues hold codes or production alerts if products deviate from desired quality standards. This can avert the release of substandard products and wasted energy that goes into making and recycling the batch. Furthermore, MES facilitates scrap tracking, enabling decision makers to discern reasons behind product rejection and minimizing recurring issues. Complete Tracking / Genealogy Uninterrupted visibility across the entire production spectrum is one of the biggest benefits of an MES system in steel production. It provides a comprehensive view of the mill from tracing raw materials to finished products. The system adeptly tracks the lot, including piece-level inventory, work-in-progress, materials on hold, and finalized goods awaiting shipment. The inclusion of product traceability ensures access to historical data, delineating the manufacturing origin for each metal piece. Closing Thoughts The impact of MES in steel production is substantial, given its potential to optimize the entire production process. With numerous companies still operating in steel production without embracing full digitization, there exists ample opportunity to enhance competitiveness in the market. As seasoned workers retire, technology becomes crucial to compensate for
Read MoreMES and the Digital Twin: Enhancing Product Lifecycle Management
Table of content Understanding MES: A Catalyst for Operational Excellence Digital Twins: An Overview Integration of MES and Digital Twins Conclusion In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, the integration of advanced technologies has become imperative for staying competitive and efficient. Two key technologies, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Digital Twins, have emerged as powerful tools for optimising the Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) process. This article explores the synergies between MES and Digital Twins, delving into how their integration enhances PLM, streamlines operations, and contributes to overall business success. Understanding MES: A Catalyst for Operational Excellence Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and the shop floor. MES provides real-time visibility and control over manufacturing operations, offering a comprehensive set of functionalities to improve efficiency, traceability, and compliance. Real-time Data Collection and Analysis One of the fundamental features of MES is its ability to collect and analyse real-time data from various sources on the shop floor. This includes data from machines, sensors, and manual inputs. By aggregating this information, MES provides a holistic view of the production process, enabling quick decision-making and proactive problem-solving. Shop Floor Visibility MES enhances shop floor visibility by providing real-time insights into the status of production processes. This transparency helps manufacturers identify bottlenecks, optimise resource allocation, and ensure that production is aligned with demand. This increased visibility is crucial for meeting customer expectations and maintaining a competitive edge. Quality Management Quality is a critical factor in manufacturing, and MES plays a vital role in ensuring product quality throughout the production process. MES systems facilitate real-time monitoring of product quality, allowing for early detection of defects and deviations. By implementing automated quality checks, manufacturers can reduce the risk of defects, minimise rework, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction. Traceability and Compliance Traceability is a key requirement in many industries, especially those with stringent regulatory standards. MES enables end-to-end traceability by capturing and recording data related to materials, processes, and finished products. This not only ensures compliance with regulatory requirements but also helps in quickly identifying and addressing any issues that may arise. Digital Twins: An Overview Digital Twins are virtual representations of physical objects or systems. In the context of manufacturing, a Digital Twin mirrors the entire lifecycle of a product, from design and prototyping to manufacturing and maintenance. This digital replica allows manufacturers to simulate, monitor, and analyse the behaviour and performance of the physical product in real-time. Design and Prototyping At the beginning of the product life cycle, Digital Twins are used to create virtual prototypes. This enables designers and engineers to simulate various scenarios, test functionalities, and identify potential issues before physical prototypes are built. By doing so, manufacturers can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with the design phase. Manufacturing Simulation During the manufacturing phase, Digital Twins simulate the production process. Manufacturers can analyse the impact of different variables, such as machine settings and production schedules, on the final product. This simulation capability helps in optimising production workflows, minimising downtime, and improving overall efficiency. Predictive Maintenance Digital Twins continues to add value during the operational phase by facilitating predictive maintenance. By monitoring the performance of physical assets in real-time, manufacturers can predict when maintenance is required, reducing the risk of unplanned downtime and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Performance Monitoring and Optimization Throughout the entire product lifecycle, Digital Twins enables continuous performance monitoring. Manufacturers can analyse data from sensors embedded in physical assets to identify patterns, optimise processes, and enhance overall performance. This iterative improvement loop contributes to a more efficient and cost-effective production environment. Integration of MES and Digital Twins While MES and Digital Twins each offer unique benefits, their integration creates a powerful synergy that enhances PLM comprehensively. The combination of real-time operational data from MES and the simulation capabilities of Digital Twins allows manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimise processes, and ensure the seamless flow of information across the entire product lifecycle. Improved Decision-Making through Data Fusion The integration of MES and Digital Twins allows for the fusion of real-time data from the shop floor with the virtual representation of the product. This data fusion provides a comprehensive view of both the current state of production and the expected behaviour of the product throughout its lifecycle. Manufacturers can make data-driven decisions that align with business objectives, leading to improved overall efficiency. Enhanced Product Quality and Innovation By leveraging Digital Twins in conjunction with MES, manufacturers can enhance product quality and drive innovation. Virtual prototypes can be linked to real-time data from production processes, enabling a closed-loop feedback system. Any deviations between the virtual and physical models can be quickly identified and rectified, ensuring that the final product meets the desired quality standards. Streamlined Change Management Change management is a constant in manufacturing, whether it involves design modifications, process adjustments, or supply chain alterations. The integration of MES and Digital Twins streamlines change management by providing a unified platform for evaluating the impact of proposed changes. Manufacturers can simulate the effects of changes in the virtual environment before implementing them in the physical production process, reducing the risk of disruptions. Optimised Production Processes The combination of MES and Digital Twins enables the optimization of production processes by identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Real-time data from MES allows for the monitoring of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) on the shop floor, while Digital Twins simulate the impact of process changes. This dual approach facilitates continuous improvement, leading to higher productivity, reduced costs, and improved resource utilisation. Lifecycle Visibility and Collaboration Integrating MES and Digital Twins enhances collaboration and visibility across the entire product lifecycle. All stakeholders, from design engineers to production managers, can access a unified platform that provides a real-time view of the product’s status and performance. This fosters better communication, collaboration, and coordination among different departments, ultimately contributing to more efficient and synchronised operations. Conclusion The integration of MES and Digital Twins represents a transformative approach to enhancing Product Lifecycle Management. By combining the real-time
Read MoreMES and Industry 4.0: The Smart Factory Revolution
Table of content Understanding Industry 4.0 Key Pillars of Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) The Integration of MES and Industry 4.0 Challenges and Considerations Conclusion In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the convergence of digital technologies has given rise to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0. At the heart of this revolution is the integration of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), playing a pivotal role in transforming traditional factories into smart factories. This article explores the synergy between MES and Industry 4.0, shedding light on how these technologies are reshaping the manufacturing sector and ushering in a new era of efficiency, flexibility, and innovation. Understanding Industry 4.0 Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing, characterised by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological systems. It leverages advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and cyber-physical systems to create intelligent, interconnected production environments. The goal is to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and enable greater customisation in manufacturing processes. Key Pillars of Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) MES acts as the bridge between the shop floor and the enterprise level in manufacturing. It provides real-time visibility into production processes, allowing for effective control and optimisation. MES encompasses a range of functionalities, including production scheduling, quality management, inventory tracking, and performance analysis. As the digital backbone of smart factories, MES facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among different components of the manufacturing ecosystem. The Integration of MES and Industry 4.0 The convergence of MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and Industry 4.0 represents a pivotal transformation in the manufacturing landscape, heralding a new era of interconnected, intelligent production. This integration is at the core of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, where digital technologies seamlessly meld with traditional manufacturing processes, redefining the way factories operate. Challenges and Considerations While the integration of MES and Industry 4.0 offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation. Conclusion The synergy between MES and Industry 4.0 is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, ushering in the era of smart factories. By leveraging the power of real-time data, IoT, AI, and other advanced technologies, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, flexibility, and innovation. The integration of MES acts as a catalyst, providing the necessary connectivity and control to realise the full potential of Industry 4.0. As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, companies must embrace this transformative journey, addressing challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented by MES and Industry 4.0. The smart factory revolution is not just a technological advancement; it is a paradigm shift that demands a holistic approach encompassing technology, workforce development, and a strategic vision for the future of manufacturing. Those who successfully navigate this shift will position themselves as industry leaders, driving the next wave of innovation in the global manufacturing landscape. Embrace the future of manufacturing with Prescient–your partner in MES and Industry 4.0 solutions. Unlock the full potential of smart factories, enhance efficiency, and stay ahead in the competitive landscape. Contact us today to embark on your journey towards a connected and innovative manufacturing ecosystem.
Read MoreEnsuring Compliance and Traceability with MES in Discrete Manufacturing
Table of content Understanding MES in Discrete Manufacturing Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Challenges Traceability in Discrete Manufacturing Real-time Data Collection and Monitoring Integration with ERP Systems Electronic Batch Records (EBR) and Documentation Quality Management and Compliance Audits Supply Chain Visibility and External Collaboration Continuous Improvement and Adaptability Conclusion In the dynamic landscape of discrete manufacturing, companies face increasing pressure to meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency. Compliance and traceability have become critical aspects of modern manufacturing, with regulatory bodies imposing strict standards to ensure product quality, safety, and transparency. To navigate this complex terrain, many manufacturers turn to Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) as a strategic solution. This article explores the role of MES in ensuring compliance and traceability in discrete manufacturing and highlights its impact on operational excellence. Understanding MES in Discrete Manufacturing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) serve as a bridge between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and the shop floor. MES provides real-time data, visibility, and control over various manufacturing processes, enabling organisations to optimise production, minimise waste, and enhance overall efficiency. In the context of compliance and traceability, MES plays a pivotal role in capturing, storing, and managing data related to every stage of production. Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Challenges The discrete manufacturing sector operates in an environment characterised by a myriad of regulations and standards. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining consumer trust and brand reputation. Whether it is adherence to quality standards, environmental regulations, or safety protocols, manufacturers must navigate a complex web of compliance requirements. MES aids in compliance by providing a centralised platform for monitoring and enforcing adherence to regulatory standards. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, where compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is paramount, MES ensures that each step in the manufacturing process aligns with the prescribed guidelines. Real-time monitoring and documentation capabilities help companies demonstrate compliance during audits, reducing the risk of penalties and legal consequences. Traceability in Discrete Manufacturing Traceability is the ability to track and trace the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products throughout the entire supply chain. This is crucial for identifying and addressing issues such as product defects, recalls, or compliance deviations. MES facilitates traceability by capturing and storing data related to each production step, creating a comprehensive digital thread that follows the product lifecycle. In the automotive industry, for example, traceability is not only a regulatory requirement but also a strategic need. MES allows manufacturers to trace the origin of each component, monitor the production process in real-time, and link the final product to specific batches of raw materials. This level of traceability enhances quality control, expedites root cause analysis in case of defects, and enables quick response to any recalls. Real-time Data Collection and Monitoring One of the key features of MES is its ability to collect and process real-time data from various sources on the shop floor. This includes data from machines, sensors, and manual inputs by operators. Real-time monitoring ensures that any deviations from predefined standards are immediately identified, allowing for prompt corrective action. For instance, if a critical parameter in the production process deviates from the set range, MES can trigger alerts and notifications to relevant personnel. This enables proactive intervention to prevent quality issues and ensures that the manufacturing process remains within the specified compliance parameters. Real-time data also provides valuable insights for continuous improvement, helping organisations optimise their processes for efficiency and quality. Integration with ERP Systems MES is most effective when seamlessly integrated with other enterprise systems, particularly ERP systems. This integration ensures a smooth flow of information between different business functions, from order management to production planning and execution. By connecting MES with ERP, manufacturers can achieve end-to-end visibility and control over the entire value chain. For compliance, this integration is crucial as it allows MES to access and utilise data from ERP systems, such as product specifications, quality standards, and customer requirements. This ensures that the manufacturing process aligns with the broader business objectives and meets the necessary compliance criteria. Moreover, it streamlines data exchange, reducing the likelihood of errors and discrepancies that may arise from manual data entry. Electronic Batch Records (EBR) and Documentation In regulated industries, maintaining accurate and comprehensive records is non-negotiable. MES facilitates the creation of Electronic Batch Records (EBR), replacing traditional paper-based documentation with digital records. EBRs capture every detail of the production process, including raw material quantities, equipment used, environmental conditions, and personnel involved. The advantages of EBRs are manifold. They not only eliminate the risks associated with manual record-keeping, such as data entry errors and document loss but also make information easily accessible for audits or inspections. With MES, manufacturers can generate a complete and accurate history of each batch or product, demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements and standards. Quality Management and Compliance Audits Quality management is intrinsically linked to compliance in discrete manufacturing. MES enhances quality control by providing tools for real-time quality monitoring, statistical process control, and automated inspections. By integrating quality management functionalities, MES helps identify and rectify defects during production, preventing non-compliant products from reaching the market. Additionally, MES supports compliance audits by offering a centralised repository of production data and documentation. During audits, regulatory bodies can access the necessary information quickly and efficiently. This not only expedites the audit process but also instils confidence in the manufacturer’s commitment to compliance. Supply Chain Visibility and External Collaboration The discrete manufacturing process extends beyond the boundaries of a single facility. Suppliers, contract manufacturers, and other external partners play crucial roles in the supply chain. MES facilitates end-to-end visibility by connecting different stakeholders and ensuring that compliance requirements are communicated and met across the entire network. For example, in the aerospace industry, where strict regulations govern the production of components, MES enables collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers. By sharing real-time production data and quality metrics, manufacturers can ensure that components meet the required specifications, fostering a transparent and compliant supply chain. Continuous Improvement and Adaptability Compliance is not a
Read MoreEnergy Management in Process Manufacturing: A Role for MES
Table of content Understanding Process Manufacturing The Challenge of Energy Management The Role of MES in Energy Management Overcoming Challenges and Implementation Considerations Future Trends and Innovations Conclusion In the dynamic landscape of process manufacturing, optimising energy consumption has become a critical concern. As industries strive to achieve sustainability goals and reduce their environmental footprint, effective energy management has emerged as a key strategy. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a pivotal role in this endeavour by providing the tools and insights necessary to monitor, control, and optimise energy usage throughout the production process. Understanding Process Manufacturing Process manufacturing involves the conversion of raw materials into finished products through a series of chemical, physical, or biological transformations. Industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and oil and gas are prominent examples. Unlike discrete manufacturing, where individual units are produced separately, process manufacturing involves continuous or batch production methods. In these complex operations, energy-intensive processes are integral to the production cycle. Heat, electricity, and other forms of energy are crucial inputs, and their efficient utilisation directly impacts production costs, product quality, and environmental sustainability. The Challenge of Energy Management The challenge in process manufacturing lies in striking the right balance between production efficiency and energy consumption. Often, plants face difficulties in identifying energy wastage, understanding consumption patterns, and implementing effective measures to optimise energy usage. This is where MES steps in as a powerful ally. The Role of MES in Energy Management Real-Time Monitoring and Data Acquisition MES platforms enable real-time monitoring of various production parameters, including energy consumption. By integrating with sensors and control systems, MES captures data on equipment performance, production rates, and energy usage. This real-time visibility empowers plant managers to identify inefficiencies, detect anomalies, and take corrective actions promptly. Historical Data Analysis Beyond real-time monitoring, MES facilitates the analysis of historical data. By examining trends and patterns in energy consumption over time, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into the factors influencing efficiency. This historical perspective is crucial for identifying long-term trends, setting benchmarks, and formulating strategies for continuous improvement. Energy Performance Metrics MES provides a comprehensive set of energy performance metrics that serve as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for evaluating the efficiency of energy usage. These metrics may include energy intensity per unit of production, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) from an energy perspective, and energy cost per unit. By tracking these metrics, manufacturers can assess their energy performance, compare it against industry benchmarks, and prioritise areas for improvement. Integration with Control Systems MES seamlessly integrates with control systems, allowing for a holistic approach to energy management. By interfacing with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS), MES can dynamically adjust production parameters based on real-time energy data. This integration ensures that energy-saving measures are implemented in response to changing production conditions, maintaining the delicate balance between efficiency and output. Demand Response and Peak Load Management Process manufacturing often involves dealing with fluctuating energy prices and demand variations. MES enables proactive energy management strategies such as demand response and peak load management. By analysing historical data and market trends, MES can help plants schedule energy-intensive processes during periods of lower demand or when energy prices are more favourable, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Overcoming Challenges and Implementation Considerations While the benefits of MES in energy management are evident, successful implementation requires careful consideration of various factors: System Integration Integrating MES with existing control systems, sensors, and other data sources is crucial for seamless data flows. Compatibility and interoperability with the plant’s existing infrastructure should be thoroughly assessed to ensure a smooth implementation process. Scalability As manufacturing processes evolve, the MES solution must be scalable to accommodate changes in production volumes, product lines, and energy requirements. A scalable MES can adapt to the dynamic nature of process manufacturing and continue to deliver value over the long term. Employee Training and Change Management The successful adoption of MES for energy management relies on the engagement and understanding of plant personnel. Providing comprehensive training programs and implementing effective change management strategies are essential to ensure that operators, engineers, and managers are aligned with the goals of energy optimisation. Data Security Given the sensitive nature of production data, ensuring the security of information within the MES platform is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures must be in place to protect against unauthorised access, data breaches, and other potential threats. Regulatory Compliance Industries, especially those in pharmaceuticals and chemicals, are subject to stringent regulatory requirements. The MES solution should support compliance with industry-specific regulations related to data integrity, traceability, and reporting. Future Trends and Innovations As technology continues to advance, the role of MES in energy management is poised to evolve. Several trends and innovations are likely to shape the future of energy optimisation in process manufacturing: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into MES platforms will enhance the ability to predict, analyse, and optimise energy consumption. These technologies can identify subtle patterns in data, recommend optimal operating conditions, and even predict equipment failures before they occur. Edge Computing Edge computing brings processing power closer to the data source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making. MES solutions leveraging edge computing can provide instantaneous insights into energy usage, allowing for immediate adjustments to optimise efficiency. Digital Twins The concept of digital twins involves creating virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems. In the context of process manufacturing, creating digital twins of production lines can facilitate advanced simulations and scenario analysis for energy optimisation. MES integrated with digital twin technology can offer a powerful tool for experimenting with different energy management strategies in a risk-free virtual environment. Energy Blockchain Blockchain technology, known for its transparency and security, holds the potential for revolutionising energy management. In a blockchain-based system, energy transactions and data sharing can be securely recorded and verified, promoting trust among stakeholders and facilitating the creation of decentralised energy grids. Conclusion Energy management is a critical aspect of achieving sustainability goals and maintaining
Read MoreDiscover How MES Enhances Discrete Manufacturing in the Age of Industry 4.0 and Boosts Productivity
Table of content Introduction How MES Enhances Discrete Manufacturing in the Age of Industry 4.0 MES Implementation Best Practices: Making Integration Smooth Overcoming Challenges in Using MES for Discrete Manufacturing Conclusion Introduction Industry 4.0 reshapes product creation in the manufacturing industry. This guide focuses on Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) in discrete manufacturing and highlights how MES boosts productivity. Navigate through Industry 4.0 complexities and uncover how MES manages shop floor information to ensure precision and effectiveness. How MES Enhances Discrete Manufacturing in the Age of Industry 4.0 In the world of making things, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are like a guiding force, especially as we step into the era of Industry 4.0. Let’s break down how MES makes a big difference in making things efficient in the modern age. Making Smart Decisions in Real Time MES keeps an eye on everything happening during production. This helps decision-makers have the latest information instantly. Whether it is adjusting schedules, making the best use of machines and people, or dealing with unexpected issues, MES ensures decisions are quick and well-informed. Getting Production Schedules Right MES is like a scheduling wizard. It adjusts production plans on the fly, considering things like machine availability, workforce capacity, and order priorities. This wizardry minimizes downtime and makes sure everything runs smoothly to meet market needs most smartly. Top-Notch Quality Control MES is all about making sure everything that is produced is top-notch. It keeps a close eye on quality at every step, using checks and controls to catch and fix any problems. MES also helps trace each product’s journey through production, making it easier to find and fix quality issues. Keeping Track of Inventory and Supplies MES does not stop at the production line; it also helps with keeping track of materials and supplies. By giving real-time info on inventory, MES makes sure there’s just enough stock, avoiding extra costs and preventing shortages. It also works hand-in-hand with supply chain systems, making sure everything is in sync and ready to meet changes in demand. Getting Along with New Technology MES is like a friend to all the cool new technologies of Industry 4.0, like smart devices and smart analysis. By teaming up with these technologies, MES makes manufacturing not just efficient but also ready for the future. It’s like having a buddy that helps adapt to whatever the digital age throws our way. MES Implementation Best Practices: Making Integration Smooth Bringing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) into discrete manufacturing requires thoughtful planning for a successful integration. Let’s explore practical tips and considerations to ensure a smooth implementation of MES into daily operations. Making Systems Work Together Ensure MES fits well with existing systems like ERP and CRM. This integration should flow seamlessly, minimizing disruptions and creating a well-connected digital setup. Training and Helping Employees Adapt Proper training is key. Help the workforce not just understand the new system but use it effectively. Also, manage changes by communicating, providing support, and involving key players in the process. Growing with the Flow Plan for growth. Make MES flexible enough to adapt to changes in production volume, product lines, or new tech. This ensures the system stays useful even as manufacturing needs evolve. Keeping Data Safe With interconnected systems, protect sensitive manufacturing data. Use encryption, access controls, and regular security checks to keep the information secure and instill confidence in users. Thorough Testing Before going live, test MES thoroughly. Simulate different scenarios to catch and fix any issues. This helps avoid disruptions during actual use and builds trust in the reliability of the MES solution. Working Together with Vendors Collaborate closely with MES vendors. Regular communication, quick issue resolution, and ongoing support ensure a smooth journey. Building a strong partnership with the vendor enhances the effectiveness and longevity of the MES solution. Overcoming Challenges in Using MES for Discrete Manufacturing Bringing in Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) has many advantages for discrete manufacturing, but there are some challenges to tackle. Let’s break down these challenges and find simple solutions to make sure MES works smoothly in the world of making things. Making Different Systems Work Together MES might find it hard to connect with existing systems, causing integration issues. Choose MES that easily fits with different systems. Use middleware if needed, like a helpful bridge connecting MES with other software or machines. This way, information can flow smoothly across all parts of the production process. Getting Everyone Onboard Some workers may not want to use new tech, making it a challenge to get everyone on the same page. Teach everyone how MES helps. Show them how it makes tasks easier, improves work, and makes everything run more smoothly. By giving proper training, everyone can see the benefits and feel positive about using MES. Counting the Costs Getting MES up and running can be costly in the beginning, which might be a concern for some organizations. Look at the bigger picture. MES can save money in the long run by making things more efficient and reducing mistakes. Emphasize these advantages to show how the initial cost is worth it for the benefits it brings. Keeping Information Safe Storing important production data safely is a worry for many, considering data security. Use strong security measures, like keeping data encrypted and controlling who can access it. Follow the rules about data protection and regularly check for any security issues. This builds trust that important information is handled securely. Making MES Fit Just Right Making MES fit exactly with specific manufacturing needs can be tricky. Pick MES that can be adjusted to fit what’s needed. Choose vendors who understand how things work in your making process. This way, MES can be changed without causing problems. Growing Without Problems MES might struggle when operations grow, making it hard to adapt to changes. Choose MES that can grow with the organization. Make sure it can handle more data, more users, and new things to do without slowing down or encountering hiccups. Getting Used to a New Way
Read MoreA Guide to Choosing the Right Vision Based Inspection System
Table of content Introduction What Can Vision Based Inspection Systems Do? Vision Based Inspection Examples Steps to Choose the Right Vision based Inspection System 1. The Inspection System Should be AI Driven 2. Look for Specialization in Your Industry 3. Go Through Customer Reviews 4. Choosing for employee Safety Conclusion Introduction Vision inspection systems harness automated digital imaging to fulfill crucial manufacturing tasks. These tasks encompass steps that require a high degree of precision such as quality control, sorting, and verification. Regarded as indispensable by industrialists today, the technology liberates production line staff for more strategic roles leaving the cumbersome work to the machines. Efficiency of the vision inspection system lies in their high-speed operation, which results in significant time and cost savings for manufacturers. These systems excel in rapid data processing and continually improve through artificial intelligence integration. Furthermore, their capability to generate high-resolution images allows operators to scrutinize product defects with exceptional detail, contributing to less errors in the manufacturing process. In this article, we take a closer look at some of the vision-based inspection solutions and choose one that is right for you. What Can Vision Based Inspection Systems Do? Intelligent inspection systems are often equipped with multiple cameras, along with video and lighting features. These vision systems excel in measuring parts, verifying their correct positioning, recognizing shapes and more. Capable of high-speed measurement and sorting, they employ computer software to process captured images during the assessment process, extracting valuable data. Integration into production lines allows these systems to offer a continuous flow of information, ensuring real-time insights and efficient decision-making for enhanced operational precision. Vision Based Inspection Examples Here are some of the frequently used vision inspection systems in different industries: Steps to Choose the Right Vision based Inspection System While you may already know precisely the vision-based inspection you need for your industry, choosing the system goes well beyond the technology. It is equally important to choose the right partner/vendor who can deliver precisely what you need and ease the process of implementation. So here’s how you arrive at your solution before implementing vision based inspection: 1. The Inspection System Should be AI Driven Legacy systems with simple programming have been the standard since visual-based inspection came into existence. However, AI reinforcement can fundamentally augment detection systems and increase the scope of error detections in production. Visual-based Inspection, powered by deep learning algorithms, elevates the process by enabling the differentiation of parts, characters, and anomalies. This mirrors the capacity of human visual defect detection while leveraging the computational efficiency of a computer system. What’s more, unlike human operators who are subject to fatigue and experience, the AI system performs consistently. 2. Look for Specialization in Your Industry Selecting a vision-based inspection system tailored to your industry can make a significant difference. Opting for a partner specializing in your specific sector is not merely a matter of cost; it is an investment in precision and expertise. Entrusting an experienced partner even if their service may entail a slightly higher cost, outweighs the risks of inexperienced handling. A specialized partner comprehends the intricacies of your industry, foreseeing and addressing impending challenges with well-tailored solutions. The decision to engage an industry-focused expert ensures the perfect integration of vision-based inspection systems, enhancing efficiency and mitigating risks associated with subpar solutions. 3. Go Through Customer Reviews When choosing a partner, go deeper into customer reviews, industry relevance, and challenges faced. Scrutinize project quality, services, timelines, duration, and costs comprehensively to avoid partnering with an unsuitable vendor. Assess their success rates and industry track record, examining their impact on businesses. Analyze their approach and ensure their solutions align precisely with your needs. Explore their client base from past and present to gauge their expertise and the breadth of industries they are able to serve. Additionally, verify if their technology is a good match for your requirements and does not fall short of any future upgrades you have planned. 4. Choosing for Employee Safety When picking vision based systems for employee safety, it is crucial to look for a solution that offers more features than what you need. For instance, the system should incorporate face recognition to detect individuals not adhering to mask or safety gadget guidelines. It should also adeptly identify damaged equipment, such as compromised harnesses, helmets, or other PPE, facilitating prompt alerts and replacements. The system must also monitor adherence to safety protocols like social distancing, machinery standard operating procedures, and plant safety protocols, instantly alerting authorities in case of non-compliance. Conclusion By adopting vision-based inspection systems, industries can harness a powerful system for precision and efficiency in manufacture. The integration of advanced cameras, software, and artificial intelligence not only boosts defect detection but also finds application in end-of-line inspections and part segregation.Now that you know the different types of vision-based systems that exist and how to choose the right tech partner for your process, it is time to take the next step! Get in touch with our team and learn how sensing technology and automation can boost your productivity today!
Read MoreAI-Driven IIoT: Exploring Algorithms for Intelligent Manufacturing
Table of content The Convergence of AI and IIoT Real-World Applications 1. Predictive Maintenance 2. Quality Control and Defect Detection 3. Supply Chain Optimization 4. Energy Efficiency 5. Process Optimization 6. Human-Robot Collaboration 7. Customized Manufacturing Challenges and Considerations Conclusion In the era of Industry 4.0, the fusion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape. Traditional manufacturing processes have given way to intelligent manufacturing systems that optimize efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality. At the heart of this transformation are advanced algorithms that harness the power of AI to analyze data, make predictions, and drive decision-making. In this article, we will delve into the world of AI-driven IIoT, exploring the algorithms that underpin intelligent manufacturing and their real-world applications. The Convergence of AI and IIoT The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, machines, and sensors within an industrial setting. These devices collect vast amounts of data, providing real-time insights into various aspects of manufacturing operations. However, this data would be overwhelming and underutilized without AI. AI algorithms bring the ability to process, analyze, and derive actionable insights from this data, making it a game-changer for the manufacturing industry. Also read How Computer Vision is Playing a Vital Role in Real Estate. Real-World Applications The application of AI algorithms in Intelligent Manufacturing is not theoretical; it is happening now and transforming industries. Here are some real-world examples of how these algorithms are making a difference: 1. Predictive Maintenance One of the most significant applications of AI-driven IIoT is predictive maintenance. Traditional maintenance strategies are often reactive, leading to costly downtime when equipment fails unexpectedly. With AI algorithms, manufacturers can predict when equipment is likely to fail based on data from sensors and historical performance. Machine learning algorithms, such as support vector machines and recurrent neural networks, analyze sensor data to identify patterns that precede equipment failure. By monitoring factors like temperature, vibration, and energy consumption, these algorithms can provide early warnings and trigger maintenance actions before a breakdown occurs. This not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of equipment, resulting in substantial cost savings. 2. Quality Control and Defect Detection Maintaining product quality is paramount in manufacturing. AI-driven IIoT enables real-time quality control by using computer vision algorithms to inspect products as they move along the production line. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are commonly employed for this purpose. These algorithms can identify defects, deviations, or anomalies in products by analyzing images captured by cameras. Any deviations from the standard can trigger alerts or adjustments in real-time, ensuring that defective products are detected and removed from the production process early, minimizing waste, and reducing rework. 3. Supply Chain Optimization Optimizing the supply chain is crucial for efficient manufacturing. AI-driven IIoT allows manufacturers to make data-driven decisions in real time to streamline logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical sales data, market trends, and production capacity to optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and ensure products are available when needed. Furthermore, AI algorithms can predict demand fluctuations, enabling proactive adjustments in production schedules and supplier orders. This ensures that supply chain disruptions are minimized, helping manufacturers maintain a competitive edge in the market. 4. Energy Efficiency Manufacturing is often energy-intensive, and optimizing energy consumption can result in significant cost savings and environmental benefits. AI-driven IIoT systems can monitor and control energy usage in real time. Reinforcement learning algorithms can optimize energy consumption by learning from historical data and adjusting the operation of machines and equipment to minimize energy usage while meeting production targets. By dynamically managing energy consumption, manufacturers can reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs. 5. Process Optimization Manufacturing processes can be complex and involve numerous variables. AI algorithms, particularly optimization algorithms, can fine-tune these processes to maximize efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality. Genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization are examples of AI techniques used for process optimization. They can search for the best combination of parameters within a given manufacturing process, helping manufacturers achieve higher yields and lower production costs. 6. Human-Robot Collaboration In intelligent manufacturing, human-robot collaboration is becoming increasingly common. AI algorithms enable robots to work alongside humans safely and efficiently. Machine learning algorithms can be used to teach robots to recognize and adapt to different human gestures and commands, making it easier for humans and robots to collaborate on tasks. Additionally, AI algorithms can optimize the allocation of tasks between human workers and robots to make the most of each party’s strengths. This leads to improved productivity and better utilization of resources. 7. Customized Manufacturing Consumer demand for customized products is on the rise, posing a challenge to traditional manufacturing methods. AI-driven IIoT systems can address this challenge by enabling mass customization. Machine learning algorithms can analyze customer preferences and historical data to predict product configurations. Robots and automated systems can then be programmed to produce customized products efficiently, catering to individual customer requirements while maintaining the efficiency of mass production. Challenges and Considerations While AI-driven IIoT offers immense benefits for intelligent manufacturing, it also presents challenges and considerations that manufacturers must address: Also read Computer Vision – The past and the present. Conclusion AI-driven IIoT has ushered in a new era of intelligent manufacturing. By harnessing the power of advanced algorithms, manufacturers can optimize processes, improve quality, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness. Predictive maintenance, quality control, supply chain optimization, energy efficiency, process optimization, human-robot collaboration, and customized manufacturing are just a few of the areas where AI algorithms are making a significant impact. As manufacturers continue to embrace Industry 4.0, it is clear that AI-driven IIoT will play a central role in shaping the future of manufacturing. While challenges exist, the potential benefits in terms of efficiency, sustainability, and product customization are too compelling to ignore. As a result, manufacturers must adapt and invest in the technologies and skills necessary to thrive in this new era of intelligent manufacturing.
Read MoreGreen Manufacturing with Digital Factories: A Sustainable Approach
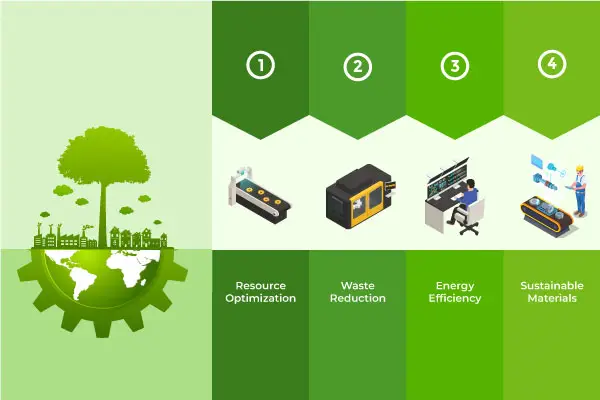
Table of content The Evolution of Manufacturing The Digital Revolution in Manufacturing The Synergy of Green Manufacturing and Digital Factories Challenges and Adoption Hurdles Conclusion Industries around the world are reviewing their procedures in an era characterized by rising environmental concerns and a greater understanding of the need for sustainability. Production is one area that is undergoing a huge transition, as the fusion of technology and sustainability is paving the way for green production and digital factories. These novel methods are increasing productivity and profitability while also minimizing the impact of manufacturing on the environment. We will discuss the idea of green manufacturing using digital factories in this post, as well as how it can help create a more sustainable future. The Evolution of Manufacturing Manufacturing has come a long way since the Industrial Revolution. In the early days, factories were notorious for the adverse environmental impacts their units had, with unchecked pollution and waste. However, over time, regulations, public awareness, and advancements in technology have forced manufacturers to rethink their practices. The concept of green manufacturing emerged as a response to these challenges. It entails minimizing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes by reducing resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions. It is about finding ways to produce goods more efficiently and sustainably. The Digital Revolution in Manufacturing The digital revolution has profoundly impacted almost every aspect of our lives, and manufacturing is no exception. Digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and automation are transforming the way products are made. Digital factories are at the forefront of this transformation. These are manufacturing facilities where digital technologies are integrated into every aspect of the production process. The key elements of digital factories include: The Synergy of Green Manufacturing and Digital Factories Sustainability is a shared objective of digital factories and green manufacturing. When these two ideas are joined, a potent synergy results that might completely alter the manufacturing sector. Challenges and Adoption Hurdles While the concept of green manufacturing with digital factories is promising, it comes with its share of challenges and adoption hurdles. These obstacles should be acknowledged and addressed to ensure a smoother transition to sustainable manufacturing practices. Despite these challenges, the future of green manufacturing with digital factories appears promising. As technology continues to advance, costs are likely to decrease, making these innovations more accessible to a broader range of manufacturers. Government incentives and regulations focused on sustainability are also expected to drive adoption. It is essential for manufacturers to acknowledge and address these challenges, working collaboratively with stakeholders to create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for the manufacturing industry. Green manufacturing with digital factories is not just a concept; it is a path to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all. Conclusion Green manufacturing with digital factories represents a sustainable approach that is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. By combining the principles of resource optimization, waste reduction, energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and supply chain sustainability, these factories are not only reducing their environmental impact but also improving their efficiency and profitability. As we move forward, it is essential for manufacturers to embrace this transformation and work collaboratively with stakeholders to create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for the manufacturing industry. Green manufacturing with digital factories is not just a concept; it is a path to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
Read MoreDigital Factory Best Practices: Optimizing Efficiency and Production
Table of content Understanding the Digital Factor Best Practices for a Digital Factor The Road to a Successful Digital Factory The traditional factory is experiencing a dramatic shift into what is frequently referred to as the “Digital Factory” in the fast-changing production scene. The adoption of cutting-edge technologies, data analytics, and automation in the production process are factors driving this transformation. A Digital Factory has one clear objective: to maximize productivity and efficiency while maintaining high product quality and adaptability. The most effective methods for achieving these goals within the framework of a digital factory have been discussed in this article. Understanding the Digital Factory Before delving into best practices, it is crucial to fully understand what a Digital Factory entails. At its core, a Digital Factory leverages digital technologies to connect and streamline every aspect of the manufacturing process. This includes automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and more. Here are some key components of a Digital Factory: Best Practices for a Digital Factory Now that we have a grasp of what a Digital Factory encompasses, let us explore the best practices for optimizing efficiency and production in this context. 1. Data-Driven Decision-Making Data is the lifeblood of a Digital Factory. To make informed decisions, it is essential to gather, analyze, and interpret data effectively. Here’s how to do it: 2. Digital Twin Implementation Digital twins provide a virtual replica of your factory, allowing you to simulate and test changes before implementing them in the real world. Key steps include: 3. Integration of Automation Automation is a cornerstone of the Digital Factory concept. Here’s how to maximize its benefits: 4. Agile and Flexible Manufacturing A Digital Factory should be adaptable to changing market demands. Here’s how to achieve agility and flexibility: 5. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy With the increased connectivity in a Digital Factory, cybersecurity becomes paramount: 6. Employee Training and Empowerment A Digital Factory is only as effective as its operators and staff: 7. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Incorporate sustainability practices into your Digital Factory: The Road to a Successful Digital Factory The journey to establishing a successful Digital Factory is not without challenges. It requires a significant investment in technology, talent, and a cultural shift towards embracing digital transformation. However, the benefits are substantial, including increased efficiency, higher product quality, and enhanced adaptability to market changes. To summarize, the best practices for optimizing efficiency and production in a Digital Factory are rooted in data-driven decision-making, digital twin implementation, automation, agility, cybersecurity, employee empowerment, and sustainability. By incorporating these practices into your manufacturing strategy, you can position your factory for success in the digital age and stay ahead of the competition. The future of manufacturing is digital, and the time to embrace it is now.
Read More