Green Manufacturing with Digital Factories: A Sustainable Approach
- Home
- Blog Details
- October 17 2023
- admin
Industries around the world are reviewing their procedures in an era characterized by rising environmental concerns and a greater understanding of the need for sustainability. Production is one area that is undergoing a huge transition, as the fusion of technology and sustainability is paving the way for green production and digital factories. These novel methods are increasing productivity and profitability while also minimizing the impact of manufacturing on the environment.
We will discuss the idea of green manufacturing using digital factories in this post, as well as how it can help create a more sustainable future.
The Evolution of Manufacturing
Manufacturing has come a long way since the Industrial Revolution. In the early days, factories were notorious for the adverse environmental impacts their units had, with unchecked pollution and waste. However, over time, regulations, public awareness, and advancements in technology have forced manufacturers to rethink their practices.
The concept of green manufacturing emerged as a response to these challenges. It entails minimizing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes by reducing resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions. It is about finding ways to produce goods more efficiently and sustainably.
The Digital Revolution in Manufacturing
The digital revolution has profoundly impacted almost every aspect of our lives, and manufacturing is no exception. Digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and automation are transforming the way products are made.
Digital factories are at the forefront of this transformation. These are manufacturing facilities where digital technologies are integrated into every aspect of the production process. The key elements of digital factories include:
- Connected Machines: IoT sensors and devices are embedded in machinery, allowing them to collect and transmit data in real-time. This data is then used to monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics tools process the vast amount of data generated by connected machines. These tools can identify inefficiencies, suggest process improvements, and help in making data-driven decisions.
- Automation: Robots and automated systems take over repetitive and dangerous tasks, improving precision and safety while reducing the need for human labor.
- Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technology is revolutionizing manufacturing by allowing products to be built layer by layer. This reduces waste and enables the creation of complex, lightweight structures that were previously impossible to manufacture.
- Digital Twin: Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets and processes. They enable manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes before implementing them in the real world, reducing trial and error and waste.
The Synergy of Green Manufacturing and Digital Factories
Sustainability is a shared objective of digital factories and green manufacturing. When these two ideas are joined, a potent synergy results that might completely alter the manufacturing sector.
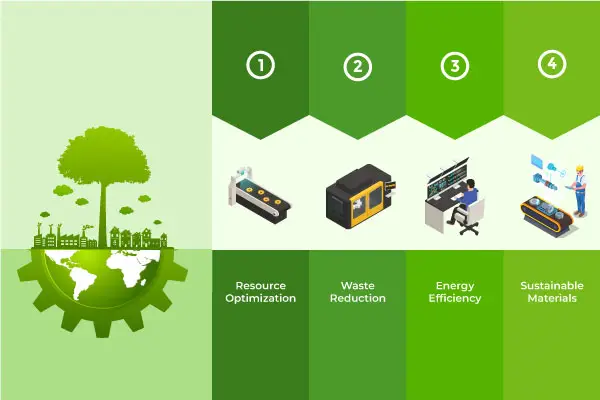
- Resource Optimization: Digital factories are adept at monitoring and optimizing resource usage. Sensors can detect variations in energy and material consumption, leading to more efficient processes. For example, real-time data can help adjust machine settings to reduce energy consumption during off-peak hours.
- Waste Reduction: Digital factories can significantly reduce waste by enabling precise control over manufacturing processes. With 3D printing, for instance, products can be built with minimal material waste. Digital twins allow manufacturers to fine-tune processes to minimize defects and scrap.
- Energy Efficiency: Through the integration of IoT and data analytics, digital factories can identify opportunities to enhance energy efficiency. Machines can be programmed to operate at optimal energy levels, and lighting and climate control systems can be adjusted based on real-time data.
- Sustainable Materials: Digital factories can explore and incorporate sustainable materials into their processes. By using recycled or bio-based materials, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on virgin resources and minimize their carbon footprint.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Digital factories are interconnected with supply chains, allowing for real-time tracking of materials and components. This transparency enables manufacturers to make informed decisions about sourcing materials from environmentally responsible suppliers.
Challenges and Adoption Hurdles
While the concept of green manufacturing with digital factories is promising, it comes with its share of challenges and adoption hurdles. These obstacles should be acknowledged and addressed to ensure a smoother transition to sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Initial Investment: Transitioning to digital factories requires a significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. Small and medium-sized manufacturers may face financial barriers to adoption, hindering the widespread implementation of these transformative technologies.
- Skilled Workforce: Operating digital factories demands a highly skilled workforce capable of managing and maintaining complex digital systems. Upskilling employees and attracting talent with expertise in digital manufacturing technologies are crucial for successful implementation.
- Data Security: With the increasing reliance on digital technologies, ensuring the security of sensitive manufacturing data becomes a critical concern. Manufacturers must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats and breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting environmental regulations can be complex, and digital factories must ensure that their operations align with local and global sustainability standards. Navigating the evolving regulatory landscape while maintaining efficiency can be challenging.
- Supply Chain Integration: Integrating digital factories into existing supply chains can be a complex task. Manufacturers need to ensure seamless coordination with suppliers, logistics, and distribution partners to fully realize the benefits of these technologies.
Despite these challenges, the future of green manufacturing with digital factories appears promising. As technology continues to advance, costs are likely to decrease, making these innovations more accessible to a broader range of manufacturers. Government incentives and regulations focused on sustainability are also expected to drive adoption.
It is essential for manufacturers to acknowledge and address these challenges, working collaboratively with stakeholders to create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for the manufacturing industry. Green manufacturing with digital factories is not just a concept; it is a path to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
Conclusion
Green manufacturing with digital factories represents a sustainable approach that is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. By combining the principles of resource optimization, waste reduction, energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and supply chain sustainability, these factories are not only reducing their environmental impact but also improving their efficiency and profitability.
As we move forward, it is essential for manufacturers to embrace this transformation and work collaboratively with stakeholders to create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for the manufacturing industry. Green manufacturing with digital factories is not just a concept; it is a path to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.

