What are Jigs and Fixtures, their Advantages, and Differences
- Home
- Blog Details
- June 12 2019
- admin
With the rapid advancement in manufacturing technology, consumerism has increased. Therefore, to meet the higher demands, manufacturers have developed innovative methods to produce high- quality products faster.
The production process has observed the introduction of inventive manufacturing concepts such as Lean Production System, Cellular Manufacturing, Single Minute Exchange of Dies, and Tact Time Analysis. These creative approaches require a horde of efficient, cheaper tools and work-holding devices.
The manufacturing company requires a simple work positioning strategy and devices for correct operations. This is to ensure:
- Non-complexities in assembly and unit cost reduction
- Reduction in the massive manufacturing cost
- Increase their profitability
The industry has resorted to easing up the supply chain to maintain. This resulted in better and cost- effective work-holding devices that ensure better quality products, increase throughput, and reduce lead time. The requirement for the production of standard work-holding devices has paved the way for two specific terms named: Jigs and Fixtures.
The jig is the device that guides the tool, while the fixture is a tool that securely and firmly holds the job in position during machining operations.
Jigs
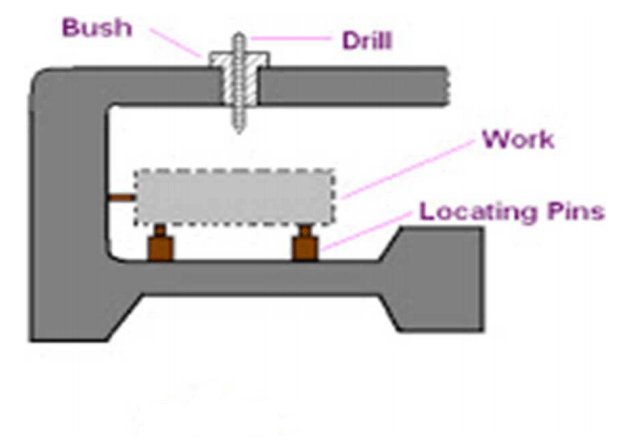
In simple terms, a jig is a tool that guides the machining tool.
A common type of jig is the drill jig, which guides the drill for making holes at desired locations. Using drill jigs increases the production rate drastically. These tools are usually made of metal, such as steel and aluminum, and are generally fitted with positioning devices called bushings. These tools guide the operation of machines and other equipment.
Fixtures
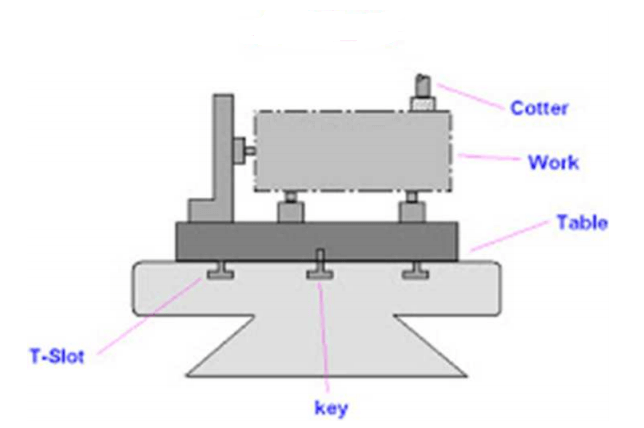
On the other hand, a fixture is a tool that firmly grips a workpiece on the machine bed accurately at the desired location.
The fixture also reduces the loading, unloading, and fixing the time of the workpiece, which significantly reduces the non-productive hours. Fixtures are used for milling, turning, and grinding operations. To ensure proper alignment and hold of parts, fixtures can include a variety of locating components. Some manufacturers are even turning to 3D printing for their fixtures.
Typical jigs and fixtures are made from Cast Iron or Aluminum, though steel versions are also available. These jigs and fixtures can be purchased or custom-built. They are mounted on T-Slot plates and hold a variety of work holding devices.
Differences between Jig and Fixture
“Jig” and “Fixture” are often referred to as synonyms, while sometimes both are used together as jigs-fixtures. Although both jig and fixture are used in the mass production process, functionally, the two are quite different tools.
Let us go through the main points which differ a Jig from a fixture.
| Jigs | Fixtures |
| A jig controls and guides the machining tool | A fixture holds and supports the component precisely for machining operations |
| Jig ensures accuracy, repeatability, and interchangeability | The fixture provides a reduction in error by holding a component firmly on a table |
| Jigs are usually on the lighter side | The fixture is bulky, rigid, and heavy |
| Jigs can be put in place and held by hand pressure | Fixtures are always placed firmly on a machine table |
| Some of the standard jig functions are drilling, reaming, tapping, and boring | Fixtures are used explicitly in milling machines, slotting machines, and shapers |
| Jigs cost more | Fixtures are not that cost-savvy compared to Jigs |
| Jigs require intricate design operations | Fixture design operations are relatively less complicated |
Advantages of Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and Fixtures have made manufacturing processes less time-consuming, more precise, and hassle-free from a human factor perspective. The benefits of jigs and fixtures include but are not limited to the following:
- Increase in production
- The consistent quality of manufactured products due to low variability in dimension
- Cost reduction
- Inter-changeability and high accuracy of parts
- Inspection and quality control expenses are significantly reduced
- The decrease in an accident with improved safety standards
- Due to relatively simple maneuverability, semi-skilled workers can operate these tools, reducing the workforce’s cost.
- The machine tool can be automated to a reasonable extent
- Complex, rigid and heavy components can be easily machined
- Simple assembly operations reduce non-productive hours
- Eliminates the need for measuring, punching, positioning, alignments, and setting up for each workpiece, thereby reducing the cycle and setting up a time
- Increases technological capacities of machine tools
- More than one device can be used simultaneously on a workpiece
- Setting higher values of some operating conditions like depth of cut, speed, and rate of feed can be attained because of the increased clamping capability of jigs and fixtures.
Both jigs and the fixtures are used to ease machining operations and reduce the non-productive time of any mass production process. The principle of location or the 3-2-1 principle, CAD tools, and FEA tools are used to design jigs and fixtures. The following article will go through more detailed information about the 3-2-1 principle and design standards of jigs and fixtures. In the manufacturing industry, innovation is often about maximizing existing resources and building on the strengths of individual companies. Focus on jigs and fixtures helps companies increase productivity and production speed and cut overall expenses. They reduce the time required for quality control, cut down on errors, and speed up the production process. Furthermore, they are easier to use, even by semi-skilled operators. And since they are standardized, they ensure that every part produced is consistent, reducing the risk of human error.
